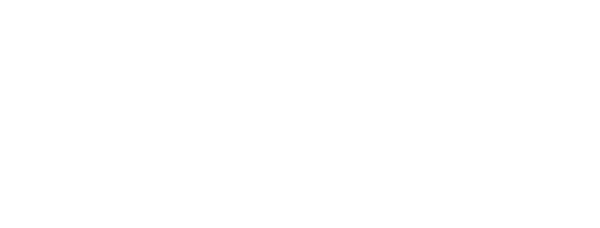Check for running processes
- Initial situation
- Checking for running programs and processes
- Select a Script
- Setting and editing a Command Set project variable
- Set and edit Command Set project variable
- Insert and customise Get process ID Command
- Command If ... Then insert and customise
- Optional: Set and edit Command Dialogs
- Inserting and customising the Else Command
- Inserting and editing an Exit script Command
- Running the Client Command through the phases
Initial situation
Sometimes it is unavoidable that you have to update software or programs that affect all or some of the Clients in your organisation, even during normal working hours. In this case, it is useful to be able to check, for example, whether a particular program is currently being actively used or not, in order to get an overview of how quickly certain updates can be deployed.
This Client Command is needed for software distribution, for example. It checks whether a particular process belonging to a programme that is to be updated is still running. The user can be informed that the program and the associated process should be closed in order to perform such an update. It does not matter whether you are checking Microsoft Word or an Internet browser. In what follows, the Command is designed to be generic, so that you can quickly adapt it specifically for other programs. For this reason, the following use case uses variables (system variables) that require very little customisation and make certain components of the script more flexible and variable.
This use case shows how you can specifically check on the clients whether a particular program or process is running. Mozilla Firefox is used as an example. You will also gain an insight into how to use variables universally.
Checking for running programs and processes
Select a Script
- Navigate to the Client Commands > Create module.
- Click Add on the ribbon bar. The Client Command Editor will open and you will need to decide whether it is a Console or Client Script. In this case select Client Script.
Setting and editing a Command Set project variable
- First select the Variables > Set Project Variable Command from the Command List.
- Double click on the Command and select the General tab.
- Enter a name under the description of the action. In this example, "Set project variable SOFTWARE_NAME to 'Mozilla Firefox'" is inserted.
- Switch to the Details tab.
- Under the variable settings, click on the icon next to the variable name.
- Optional: Create a new variable under Actions. Name it "SOFTWARE_NAME" and click on the plus icon. Then click the OK button to complete the step.
7. Enter the name of the software in the One line text box. In this example it is „Mozilla Firefox“.
8. Click OK.
Making variable settings
Set and edit Command Set project variable
- Select the Set project variable Command again.
- Double click the Command and open the General tab.
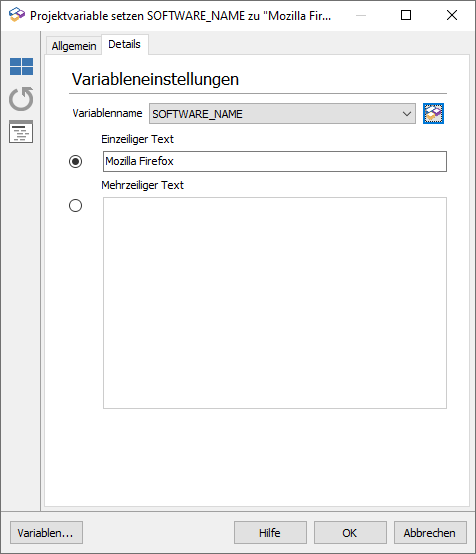
- Enter the name in the description field, e.g. Set project variable SOFTWARE_EXE to „firefox.exe“.
- Switch to the Details tab.
- Optional: Create a new variable under Actions. Name it "SOFTWARE_EXE" and click the plus icon. Click OK to complete this step.
6. Enter the process name in the Single line text box.
Enter the text „firefox.exe“.
7. Click OK.
Setting variables
Insert and customise Get process ID Command
This Command allows you to determine the current process ID of the running process or program. This makes it possible to check, in the ongoing structure of the application example, whether the particular process or program is actively running on a Client or not.
- Select the Process and Shell > Get Process ID Command.
- Double click to open the Command.
- Under Process / Target variable, enable the ... with process option by clicking the button.
- Insert the appropriate variable (%SOFTWARE_EXE%). This variable is used to check that Mozilla Firefox is running.
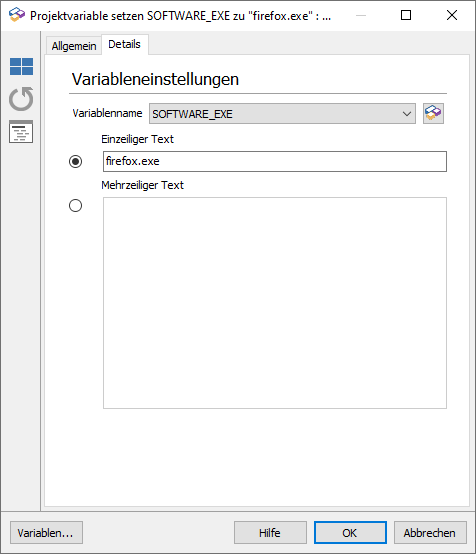
5. Under Save results in, click on the icon to the right of the variable name.
6. Open Project Variables from the drop down menu at the top.
7. Enter the name "CHECK_EXE" under the actions and click on the plus icon.
Click OK to complete this step.
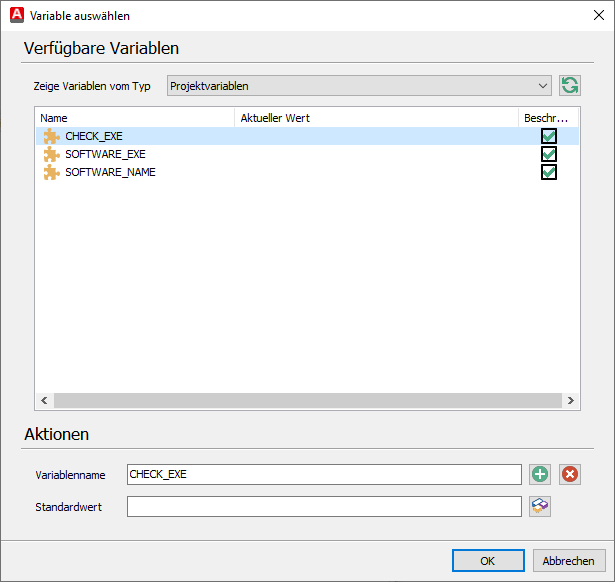
Select variable
8. The result will be stored in the CHECK_EXE variable.
9. Then click OK.

Get process ID
You have now added your first Commands to the Client Script. At this point you can check on your computer to see if the Command works. To do this, click the Start button on the quick selection bar or press the F9 key combination. This will run the first three Commands.
Now open the Run Log in the lower pane where all the logs of the Client Script are stored. Depending on whether you have the Mozilla Firefox browser open or not, you will see a different value. This is explained by the variable name "CHECK_EXE". If the variable is 0, the programme is not open. If the variable is >0, the program is open and running in the background. In the graphic shown here, the variable is set to 0, so the program is not open.
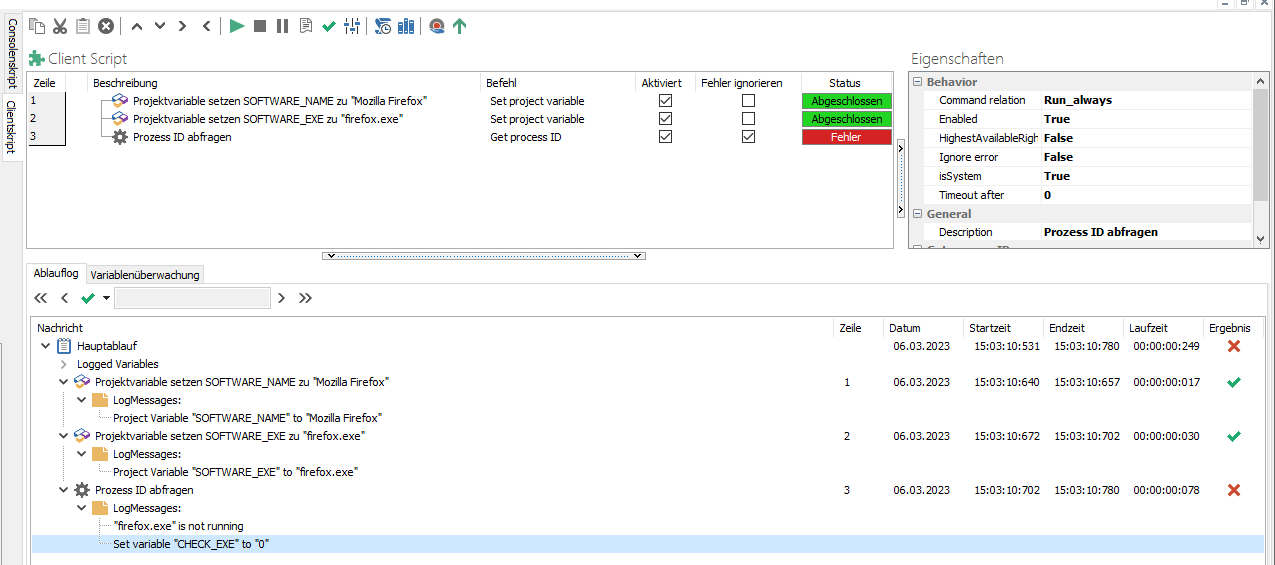
Running the Client Commands to check for running processes
Command If ... Then insert and customise
- In the Command List, select the Flow Control > If ... Command.
- Double click on the Command to open it and switch to the General tab.
- Under Action description, enter a name that describes the Command. In this example, "If (%CHECK_EXE% <> 0) Then - If the process is running ..." is written so that it is clear in the main field which condition is to be fulfilled here.
- Switch to the Details tab.
- Insert the values to be checked under the conditions. In value 1, the variable %CHECK_EXE% must be entered as this is what is to be checked. The variable in value 1 will then be filled when the programme is executed.
- Select the unequal operator (< >) to check whether the programme or process is running or not. This operator is particularly suitable because the value can always be different and you can therefore include all possibilities.
- Insert the number 0 as value 2. This is the value used as the condition for the operator.
- Click OK to complete the Command.
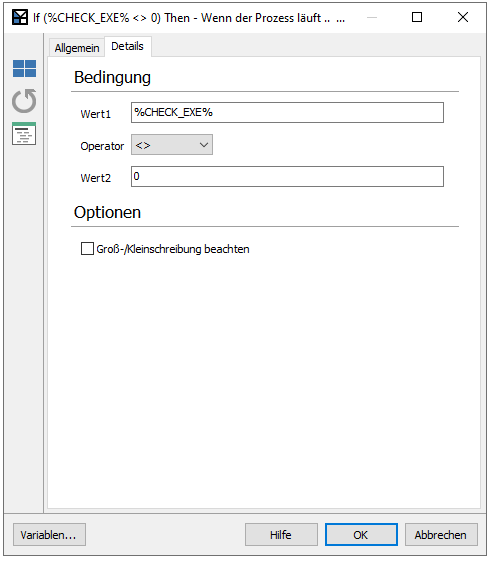
If ... Then Command
If the process is running, the row is completed as the condition is met. If the process is not running, the line is skipped.
Optional: Set and edit Command Dialogs
You can set this Command as optional if you want your Clients to see a dialogue box informing them that the program should be closed. The message can be customised. Note that the Command must be nested under the previous command (If (%CHECK_EXE% <> 0) Then) for it to work correctly.
- Select the Dialogs > Dialogs Command from the Command List.
- Open the Command by double clicking on it and open the Message Settings tab.
- Enter a suitable title for the message. Again, we recommend that you use the project variables and not the name of the program to keep the whole module variable. For example, you could write Software Update: %SOFTWARE_NAME%.
- Insert the message for the Clients to be displayed when the program is still open.
Optional: Change the message type and/or available buttons and custom captions.
5. Click OK.
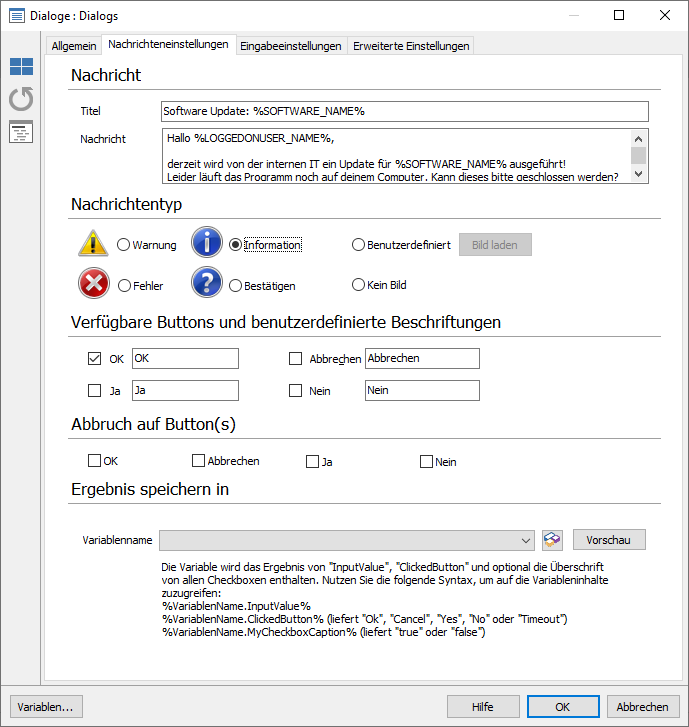
Enter a dialog
Inserting and customising the Else Command
The Else block belongs to the previous If ... Then Command. Make sure that the Command is inserted at the same level so that the conditions between If ... Then and Else are completed.
- Navigate back to the Command List and select the Flow Control > Else Command.
2. Open the Command by double clicking it.
3. Optional: Add a comment in case the Else block should be executed.
4. Click OK.
Else Command
Inserting and editing an Exit script Command
- Select Flow Control > Exit script from the Command List.
- Insert the block below the Else Command so that it is indented.
- Double click on the Command to open it.
- Select the OK condition in the Details tab. This will mark the script as successful.
5. Enter a reason why the Client Commands were successful.
6. Click OK to close the Command.
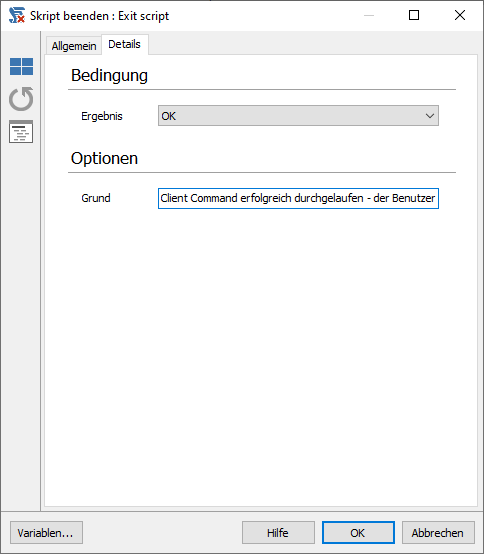
Exit Script
Your Client Script should now consist of a total of seven blocks. Save the Client Command.
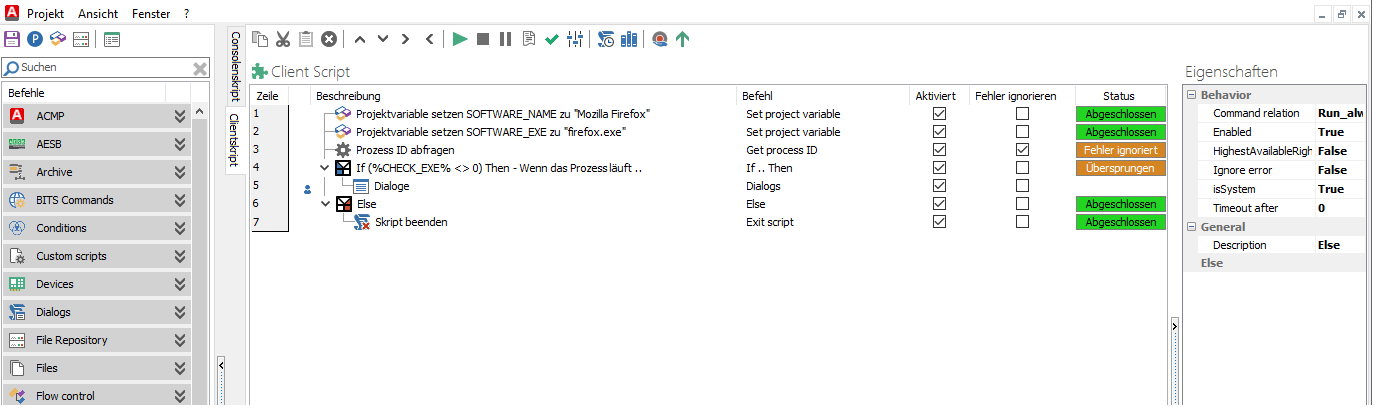
Client Command Editor: Checking for running processes
Running the Client Command through the phases
Finally, the client command must be run through the Test, Synchronise, Release and Execute phases before it can be used. This is the only way to check whether a particular program or process is actively running on a Client.